wsMed
The wsMed function is designed for two condition
within-subject mediation analysis, incorporating SEM models through the
lavaan package and Monte Carlo simulation methods. This
document provides a detailed description of the function’s parameters,
workflow, and usage, along with an example demonstration.
Installation
You can install the development version of wsMed from GitHub with:
# install.packages("pak")
pak::pak("Yangzhen1999/wsMed")
Alternatively, if you prefer using devtools, you can install wsMed as
follows:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("Yangzhen1999/wsMed")
Example
This is a basic example which shows you how to solve a common
problem:
library(wsMed)
# Load example data
data(example_data)
set.seed(123)
example_dataN <- mice::ampute(
data = example_data,
prop = 0.1,
)$amp
# Perform within-subject mediation analysis (Parallel mediation model)
result <- wsMed(
data = example_dataN, #dataset
M_C1 = c("A1","B1"), # A1/B1 is A/B mediator variable in condition 1
M_C2 = c("A2","B2"), # A2/B2 is A/B mediator variable in condition 2
Y_C1 = "C1", # C1 is outcome variable in condition 1
Y_C2 = "C2", # C2 is outcome variable in condition 2
form = "P", # Parallel mediation
C_C1 = "D1", # within-subject covariate (e.g., measured under D1)
C_C2 = "D2", # within-subject covariate (e.g., measured under C2)
C = "D3", # between-subject covariates
Na = "MI", # Use multiple imputation for missing data
standardized = TRUE, # Request standardized path coefficients and effects
)
# Print summary results
print(result)
Main Function Overview
The wsMed() function automates the full workflow for
two-condition within-subject mediation analysis. Its main steps are:
Validate inputs – check dataset structure,
mediation model type (form), and missing-data
settings.
Prepare data – compute difference scores
(Mdiff, Ydiff) and centered averages
(Mavg) from the two-condition variables.
Build the model – generate SEM syntax according
to the chosen structure:
"P": Parallel mediation
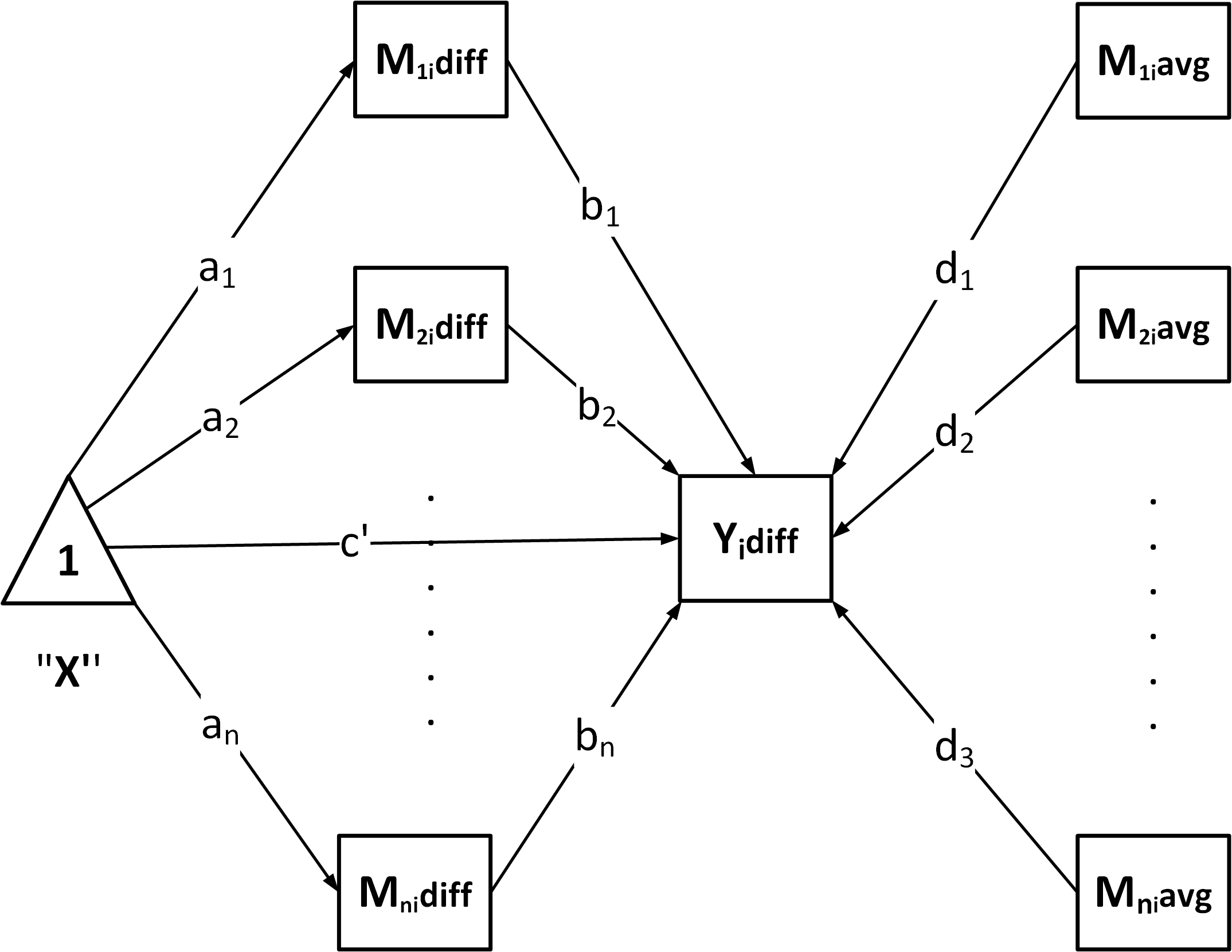
"CN": Chained / serial mediation
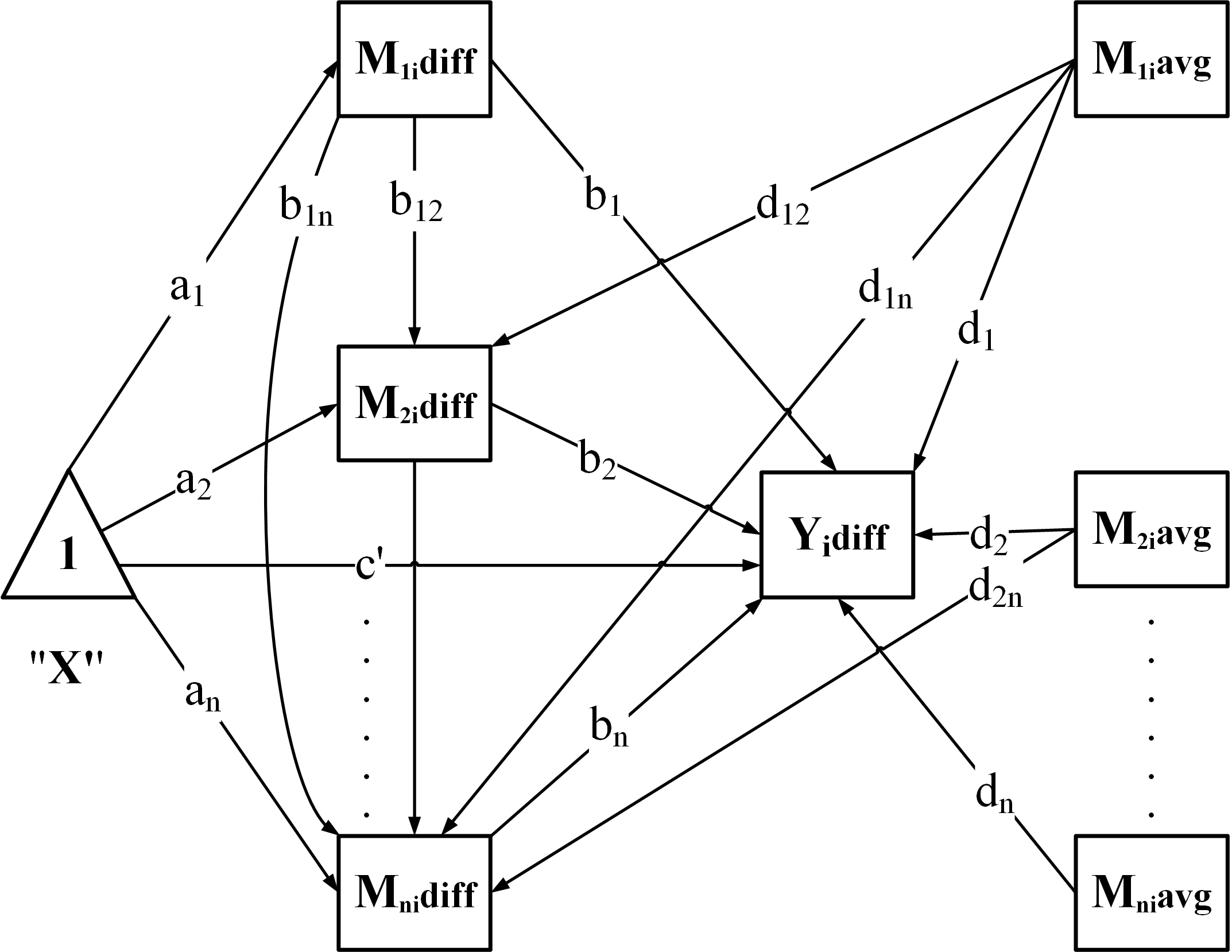
"CP": Chained + Parallel

"PC": Parallel + Chained

Fit the model – estimate parameters while
handling missing data:
"DE": listwise deletion"FIML": full-information ML"MI": multiple imputation
Compute inference – provide confidence intervals
using:
- Bootstrap
(
ci_method = "bootstrap")
- Monte Carlo (
ci_method = "mc")
Optional: Standardization – if
standardized = TRUE, return standardized effects with
CIs.
Optional: Covariates – automatically center and
include:
- Between-subject covariates (
C):
mean-centered and added to all regressions.
- Within-subject covariates (
C_C1,
C_C2): difference scores and centered averages are computed
and included.



